Hiring in the UK is attractive for global companies. The talent pool is strong, the regulatory system is transparent, and the legal framework is well-developed. But navigating the complexities of employment law in the UK can feel like wandering through a legal labyrinth.
Unlike “at-will” employment systems, UK employment law is built around statutory protections. Termination, working time, discrimination, statutory pay, pension contributions, all of it is regulated.
This guide is designed for UK employers seeking a clear overview of the key employment laws that affect their business. Understanding these laws is essential for compliance and building a positive workplace.
What is Employment Law?
Employment law is the legislation that outlines the rights and responsibilities of both employers and employees in the UK. It covers a wide range of issues, including but not limited to, age discrimination, bullying and harassment, equality, contracts, pay, and working hours.
As an employer, it is crucial to abide by these laws to ensure your employees are treated fairly and that your company remains compliant. By understanding your obligations, you can create a positive and safe work environment for your staff and avoid potential legal issues.
Why UK Employment Law Matters More in 2026?
The legal framework itself isn’t new. Most of the foundation comes from:
-
The Employment Rights Act 1996
-
The Equality Act 2010
-
The Working Time Regulations 1998
-
The National Minimum Wage Act 1998
-
The Health & Safety at Work Act 1974
The Employment Relations Act 1999 is also a key piece of legislation, regulating trade union recognition, industrial actions, and disciplinary procedures.
What has changed is enforcement intensity and legislative updates. Recent reforms, including the Employment Rights Act 2025 reforms referenced by advisory firms like Croner, introduce phased updates that affect dismissal rights, zero-hours arrangements, and statutory protections.
For global employers, this means:
-
Compliance assumptions made 3–4 years ago may no longer hold.
-
Contractor models are under greater scrutiny.
-
Dismissal flexibility is narrower than in many non-UK jurisdictions.
-
Financial exposure in tribunal claims remains significant.
(You can access the official legislation directly via https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ for full statutory wording.)
Employment Status: The First Risk Most Foreign Employers Miss
Before discussing individual laws, one issue determines everything else: employment status.
UK law recognises three primary categories:
-
Employee
-
Worker
-
Self-employed contractor
The distinction is not based on what the contract says; it’s based on the reality of the working relationship.
If there is:
-
Mutual obligation (you must offer work, they must accept it),
-
Employer control over how work is done,
-
A requirement for personal service,
The individual may legally qualify as an employee, even if labelled a contractor.
This matters because employees are entitled to:
-
Statutory notice
-
Redundancy pay
-
Unfair dismissal protection (subject to qualifying rules)
-
Full statutory leave
Misclassification can trigger retroactive liabilities for:
-
Holiday pay
-
Pension contributions
-
National Insurance
-
Notice
-
Redundancy
For global companies hiring remotely, this is one of the most common compliance failures.
Employee Rights Based on Employment Status:
It’s important to understand that employee rights can vary depending on their employment status:
-
Employee Rights: Those with an employment contract have rights such as written terms outlining their job, pay, and responsibilities, as well as sick pay, holiday pay, and parental leave pay. They can also claim redundancy and unfair dismissal after a certain period.
-
Worker’s Right: With a contract for services, workers have similar rights to employees, including written terms, the right to NMW, paid holidays, and protection against discrimination.
-
Rights for the Self-Employed: While freelancers and contractors have more flexibility, they are still protected by employment law. This includes health and safety protection when working on a client’s premises and protection against discrimination.
A Full List of UK Employment Laws & Legislations
There are several key acts and laws that embody the main parts of employment law in the UK. These include:
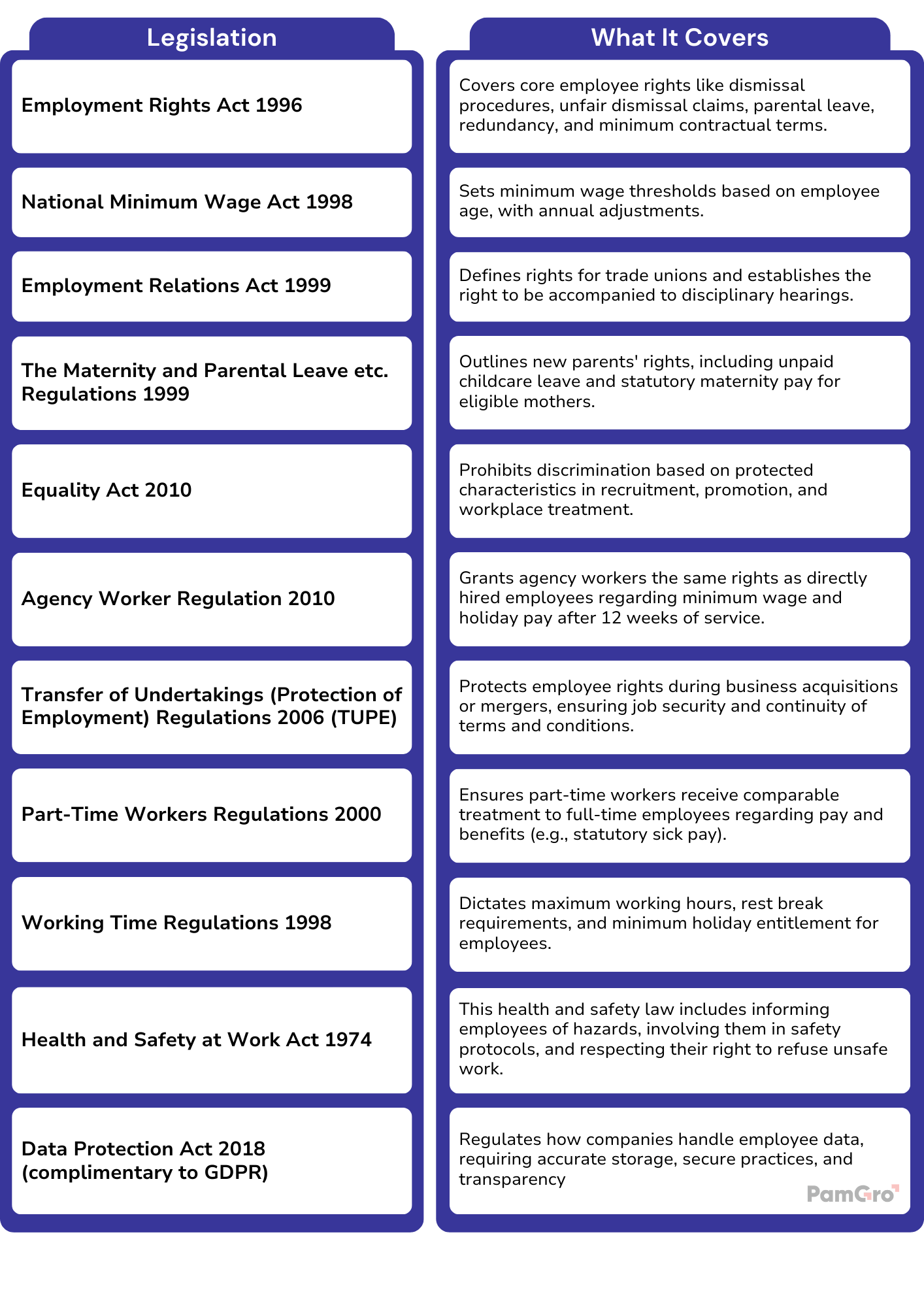
The Employment Rights Act 1996: The Core Framework
The Employment Rights Act 1996 forms the backbone of UK employment protection, setting out key employee rights under UK law.
It governs:
-
Written statements of employment particulars
-
Unfair dismissal
-
Redundancy pay
-
Statutory notice
-
Certain parental rights
For foreign employers, dismissal is where risk concentrates. This is one of the sharpest contrasts with at-will systems like the United States.
Official legislation:https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1996/18/contents
National Minimum Wage Act 1998
Employers must pay at least the statutory minimum rate based on age category. Rates are reviewed annually, typically in April.
Non-compliance can lead to:
-
Back-pay orders
-
Financial penalties
-
Public naming by HMRC
Even if payroll is processed outside the UK, local wage law still applies.
Official source:
https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1998/39/contents
Working Time Regulations 1998
These regulations establish:
-
A 48-hour average weekly working limit (unless opt-out signed)
-
5.6 weeks of statutory annual leave
-
Mandatory rest breaks
-
Night work limits
Official source:https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/1998/1833/contents
Employment Cost Calculator - UK
The Equality Act 2010: Equality & Anti-Discrimination Law
The Equality Act 2010 prohibits workplace discrimination based on protected characteristics such as age, race, sex, disability, religion, pregnancy, and sexual orientation.
The Equality Act 2010 also enforces the legal obligation of equal pay for equal work, ensuring gender pay parity and addressing discrimination in pay between men and women.
Two things matter most for global employers:
-
Discrimination claims do not require two years of service.
-
Compensation awards are uncapped.
Recent amendments, including the Worker Protection (Amendment of Equality Act 2010) Act 2023, introduced a proactive duty on employers to prevent sexual harassment. Failure can increase tribunal compensation awards by up to 25%.
This significantly increases risk exposure for companies without local HR compliance frameworks.
Official legislation:https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2010/15/contents
TUPE: The Rule That Surprises Acquiring Companies
The Transfer of Undertakings (Protection of Employment) Regulations 2006, commonly known as TUPE, apply when a business or service transfers, also referred to as a business transfer.
Under TUPE:
-
Employees transfer automatically.
-
Their terms and conditions are preserved.
-
Dismissals connected to the transfer may be automatically unfair.
TUPE regulations are specifically designed to protect employees’ rights and ensure employment continuity during a business transfer, safeguarding workers against unfair practices and maintaining job security.
For global companies acquiring UK teams, outsourcing services, or consolidating operations, TUPE compliance is critical.
Official legislation:https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2006/246/contents
Data Protection & GDPR
The UK Data Protection Act 2018 operates alongside UK GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
Severe breaches can result in fines of up to:
-
£17.5 million, or
-
4% of global annual turnover
For international companies processing UK employee data across borders, data compliance intersects directly with employment law.
Government guidance:https://www.gov.uk/data-protection
Health & Safety Obligations
The Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974 is the primary health and safety legislation in Great Britain. It requires employers to provide safe working environments and manage risk. The Act establishes legal obligations for employers and outlines worker rights regarding health and safety protections.
Employees have the right to:
-
Be informed about hazards
-
Participate in safety measures
-
Refuse unsafe work
Enforcement is handled by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), which has authority to investigate and penalise non-compliance within Great Britain.
Official legislation:https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1974/37/contents
Maternity & Parental Leave
Under the Maternity and Parental Leave Regulations 1999:
-
Up to 52 weeks maternity leave
-
Statutory maternity pay for eligible employees (structured in stages)
-
Paternity leave
-
Shared parental leave
For global companies hiring in the UK, extended leave entitlements must be built into workforce planning models.
Official legislation:
https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/1999/3312/contents
Agency Worker Regulations 2010
The regulations set out the rights of agency workers. An agency worker is entitled to the same rights as directly hired employees regarding minimum wage and holiday pay after 12 weeks of service.
Part-Time Workers (Prevention of Less Favourable Treatment) Regulations 2000:
This law requires employers to treat their part-time workers fairly compared to their full-time employees in similar job roles.
Customer Success Story
Discover how Pamgro’s Expertise helped a recruiting company for a seamless cross-border expansion across the UK and Netherlands
Other Relevant Legislation:
In addition to the rights mentioned above, there are other acts that, while not solely focused on employment, contain important information for employers:
-
Bribery Act 2010: Covers bribery, an important issue to be vigilant about in any workplace.
-
Data Protection Act 2018: Ensures businesses store employee and customer data securely and in compliance with GDPR (general data protection regulation).
-
Working Time Regulations 1998: Covers working hours and holidays, ensuring employees receive their entitled rest breaks.
What are the three basic employment rights for a worker?
Employees have three basic rights in this regard:
-
The Right to Know: Employers must inform employees of any hazards in the workplace and provide training and information on how to stay safe.
-
The Right to Participate: Employees can be involved in identifying and assessing health and safety hazards and implementing controls.
-
The Right to Refuse Unsafe Work: Employees can refuse to work if they believe it endangers themselves or others without fear of reprisal.
Tribunal Risk, Statutory Entitlements & Financial Exposure for Global Employers
Understanding UK employment law is one thing. Understanding the financial consequences of non-compliance is what actually drives strategic decisions.
For foreign companies hiring in the UK, tribunal exposure is often underestimated. The UK has a well-developed employment tribunal system, and claims are common. Even where employers ultimately succeed, defending a claim consumes time, legal cost, and management bandwidth.
Let’s break down the areas where global employers face the highest risk.
Unfair Dismissal: When Termination Goes Wrong
Under the Employment Rights Act 1996, employees can claim unfair dismissal once they meet the statutory qualifying period (subject to exceptions and evolving reforms). If an employee believes their dismissal was wrongful, they may bring an unfair dismissal claim to an employment tribunal. This process involves submitting a claim form, after which the tribunal will assess whether the dismissal was fair according to legal requirements.
To lawfully dismiss an employee, you generally need:
-
A fair reason (conduct, capability, redundancy, statutory illegality, or substantial reason)
-
A fair and documented process
-
Proper notice, meeting at least the statutory minimum notice period or any longer period specified in the employment contract
If a dismissal is found unfair, compensation typically includes:
-
A basic award (linked to age, length of service, and weekly pay)
-
A compensatory award (subject to a statutory cap, usually the lower of a fixed maximum or 52 weeks’ pay)
For global employers accustomed to at-will termination systems, the procedural requirement is the real risk. Even if performance concerns are valid, skipping process can trigger liability.
Official reference:https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1996/18/contents
Discrimination Claims: Unlimited Financial Exposure
Under the Equality Act 2010, discrimination claims are particularly serious because compensation is uncapped.
Claims can arise from:
-
Recruitment decisions
-
Promotion processes
-
Pay disparities
-
Harassment
-
Dismissal
Employees are legally entitled to bring discrimination claims from day one of employment, or even during the recruitment process.
An employee can bring a claim from day one, or even during recruitment.
Tribunals may award:
-
Financial loss
-
Injury to feelings
-
Aggravated damages
-
Recommendations
For foreign employers without established UK HR processes, this area represents one of the largest legal risks.
Recent amendments under the Worker Protection (Amendment of Equality Act 2010) Act 2023 introduced a proactive duty to prevent sexual harassment. If an employer fails to take reasonable preventative steps, tribunal compensation may be increased by up to 25%.
This significantly raises the compliance bar in 2026.
Official legislation:https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2010/15/contents
Redundancy Pay: A Statutory Obligation, Not a Negotiation
If an employee with sufficient qualifying service is dismissed due to redundancy, statutory redundancy pay may apply.
The calculation is based on:
-
Age
-
Length of service (capped at 20 years)
-
Weekly pay (subject to statutory limits)
General structure:
-
0.5 week’s pay per year under age 22
-
1 week’s pay per year between 22 and 40
-
1.5 weeks’ pay per year over 41
Foreign employers often overlook redundancy obligations when downsizing UK teams or restructuring remote operations.
This is especially relevant during:
-
Market exits
-
Post-acquisition integration
-
Budget-driven restructuring
Failure to follow redundancy consultation requirements can trigger both unfair dismissal and protective awards.
How PamGro Supports Global Companies Hiring in the UK
For companies expanding into the UK without establishing a local entity, PamGro operates as a compliant Employer of Record.
This includes:
-
Locally compliant employment contracts
-
Payroll processing aligned with HMRC requirements
-
Pension auto-enrolment management
-
Statutory leave administration
-
Ongoing compliance monitoring
-
Support with termination and restructuring processes
Instead of navigating UK employment law independently, global employers can focus on team growth while compliance infrastructure is handled locally.
This is particularly relevant in 2026 as legislative updates and enforcement continue evolving.
Wrapping Up
Understanding employment legislation is crucial for any employer, and we hope this blog has provided a comprehensive overview of the key laws and their impact. By staying informed and aware, you can create a positive and compliant work environment for your employees, fostering a culture of fairness and respect.
FAQs: UK Employment Law for Global Employers (2026)
1. Can a foreign company hire UK employees without a UK entity?
Yes, but compliance obligations still apply. Many companies use an Employer of Record to legally employ workers without establishing a local entity.
2. Is severance mandatory in the UK?
Severance is not automatically required. However, statutory redundancy pay applies where employees meet qualifying conditions and are dismissed for redundancy.
3. Do UK employees have day-one unfair dismissal rights?
Unfair dismissal protection typically requires qualifying service, although some dismissals (such as discrimination or whistleblowing-related) are protected from day one.
4. What is the biggest legal risk when hiring in the UK?
For foreign companies, the most common risks are misclassification, procedural dismissal errors, and underestimating statutory entitlements such as leave and pension contributions.
5. How does UK employment law differ from US at-will employment?
The UK requires fair reasons and proper process for dismissal. At-will termination without procedural safeguards is generally not permitted.
Payroll Solutions Unrivalled since 15 Years








