TABLE OF CONTENTS
Global mobility has become a crucial aspect of modern business strategy as organizations expand their operations across international borders. Effective global mobility programs facilitate the smooth transition of employees to new locations, helping businesses harness global talent, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge.
In essence, global mobility refers to employee relocation facilitated by organisations. By implementing comprehensive global mobility strategies, companies can effectively manage talent across borders, ensure compliance, and maximise the potential of their international workforce. Unlock the world for your talent and dive into our guide on navigating the exciting world of global mobility.
What is Global Mobility?
Global mobility or employee relocation refers to the strategic management of an organization’s workforce across different countries. This includes short-term assignments, long-term relocations, and permanent transfers of employees. The primary goal is to ensure that employees can efficiently and effectively work in different geographical locations, minimizing disruptions and maximizing productivity.
What is Global Mobility Services?
- Short Trips: Short-term assignments lasting three to twelve months for networking, contract negotiation, training, or conferences.
- Long-Term Assignments: These assignments typically last one to three years and often involve market expansion or opening new facilities abroad.
- Permanent Assignments: One-way transfers where employees take up residency in the host country indefinitely.
- Workation: A combination of work and vacation where employees continue to work from a new location for personal reasons.
- Digital Nomadism: Employees work remotely from anywhere in the world without a fixed work location.
What is the importance of Global Mobility?
1. Talent Acquisition and Retention
Filling Skill Gaps: Companies can address particular skill shortages by sourcing talent from different parts of the world. This broadens the pool of potential candidates, ensuring that the best possible individuals are hired for specialized roles.
Retaining Top Talent: Offering international career opportunities can be a significant motivator for employees. By providing opportunities for international assignments, companies can increase job satisfaction and loyalty, reducing turnover rates.
Example: A technology firm struggling to find local AI experts might look to countries with vital educational programs in AI to recruit skilled professionals. Offering these recruits a chance to work in various international offices can also enhance their job satisfaction and commitment to the company.
2. Business Expansion
Facilitates Entry into New Markets
Market Penetration: Establishing a presence in new geographical markets allows companies to reach new customer bases and expand their operational footprint.
Increased Competitiveness: By entering new markets, companies can stay ahead of competitors who operate only locally. This geographic diversification can also mitigate risks associated with economic downturns in specific regions.
Example: A retail company planning to enter the Asian market can leverage global mobility to transfer experienced managers who understand the company’s culture and operations to set up and oversee new branches, ensuring a smooth and effective market entry.
3. Cultural Diversity and Innovation
Exposure to Diverse Cultures
Fostering Creativity: Diverse teams bring varied perspectives, leading to innovative solutions and creative problem-solving. People from different cultural backgrounds can contribute unique ideas and approaches.
Broader Perspective: Working with a diverse team helps employees develop a more global outlook, which is crucial for businesses operating in multiple countries. It encourages understanding and respect for different viewpoints, enhancing teamwork and collaboration.
Example: A multinational company might establish cross-cultural teams to work on global projects, ensuring that different perspectives are considered, leading to more comprehensive and innovative outcomes.
4. Employee Development
Professional Growth Opportunities
Skill Enhancement: International assignments allow employees to gain new skills and experiences that they might not acquire in their home country. This can include language skills, cultural competence, and industry-specific knowledge.
Personal Growth: Living and working in a new or foreign country can also foster personal development. Employees learn to adapt to new environments, become more resilient, and gain a deeper understanding of global issues.
Example: An engineer sent on a long-term assignment to oversee the construction of a new plant in another country will not only gain technical and managerial skills but will also develop adaptability and cross-cultural communication abilities.
5. Adaptation to Distributed Work Models
Managing Remote and Distributed Teams
Location Flexibility: With the increasing shift towards remote work, global mobility strategies help businesses manage employees who work from various locations around the world. This ensures that operations continue smoothly, irrespective of geographical boundaries.
Support Systems: An effective and successful global mobility program includes robust support systems for remote employees, such as virtual collaboration tools, flexible work schedules, and comprehensive onboarding processes tailored for remote settings.
Example: A software company that adopts a hybrid work model might allow employees to work from anywhere, provided they maintain productivity and meet deadlines. The global mobility team ensures these employees have the necessary tools and resources to work effectively from different locations.
5 Benefits of Global Mobility
1. Broadens the Talent Pool
Global mobility breaks down geographical barriers, allowing you to tap into a worldwide pool of talent. This diverse range of skills, backgrounds, and experiences fosters innovation and fresh perspectives within your organization. Having access to a wider talent pool also empowers you to find the perfect fit for each role, ultimately improving the quality of your hires.
2. Improves Talent Retention
Today’s workforce seeks flexibility and opportunities for growth. Global mobility caters to these desires by offering international assignments and fostering a “work-from-anywhere” culture. This not only increases employee engagement by providing exciting and enriching experiences, but also strengthens retention by aligning with the needs of a mobile workforce. Companies that embrace global mobility demonstrate a commitment to employee development, leading to a more satisfied and loyal workforce.
3. Fosters Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Global mobility fosters a diverse workforce, enriching collaboration through a variety of nationalities and knowledge bases. Exposure to different backgrounds cultivates empathy and soft skills like communication and teamwork, leading to a more productive and harmonious work environment.
4. Grants Insights into New Markets
International employees offer unique insights into the markets where they reside, providing strategic advantages in competitor analysis, customer research, and branding. Their knowledge of local languages and business practices eliminates the need for additional hires, such as translators.
5. Enhances Creativity and Problem-Solving
Diverse teams bring different ideas, knowledge, and perspectives, leading to innovative solutions and enhanced problem-solving capabilities. Companies with more diverse executive teams are more likely to see better-than-average profits.
Customer Success Story
Discover how an IT services company achieved a 25% reduction in recruitment costs while improving efficiency with PamGro
5 Challenges of Global Mobility
1. Immigration
Managing the immigration and visa requirements of each country where employees reside is complex. Employers must choose proper visas, provide sponsorship, collect documentation, pay fees, and ensure timely renewals. Compliance oversights can trigger hefty fines and stall your expansion.
2. Employment Law and Taxes
Operating globally demands adherence to local employment and tax laws. From setting up compliant contracts to navigating minimum wage by country, income tax, and benefits regulations, companies must tread carefully. Oversights can lead to hefty fines, back pay, tax arrears, and even restricted business opportunities. Partnering with top legal teams and tax specialists can help navigate these complexities and ensure smooth global expansion.
3. Compensation
Maintaining compliant compensation across markets is key. Base salaries should factor in minimum wage, living costs, and pay equity laws in each location. Complementing this with locally relevant benefits shows your commitment to employee well-being and attracts top talent. Think beyond basic packages and tailor offerings to local preferences and needs, ensuring your global workforce feels valued and supported.
4. Permanent Establishment
Employing talent worldwide can create a permanent establishment (PE) in a host country, triggering a local corporate tax liability. PE laws vary globally, but even short-term work assignments can indicate PE in many jurisdictions. To mitigate this risk, some companies establish local entities, a lengthy and costly process requiring significant long-term investments.
5. Cultural Acclimation
International relocations can be daunting for employees and families. Supporting their cultural adjustment is crucial for well-being and minimizing churn. From navigating language barriers and time zone differences to understanding local customs, offering pre-departure training and ongoing support eases the transition and fosters a smoother integration into the new environment.
How to Develop a Global Mobility Strategy?
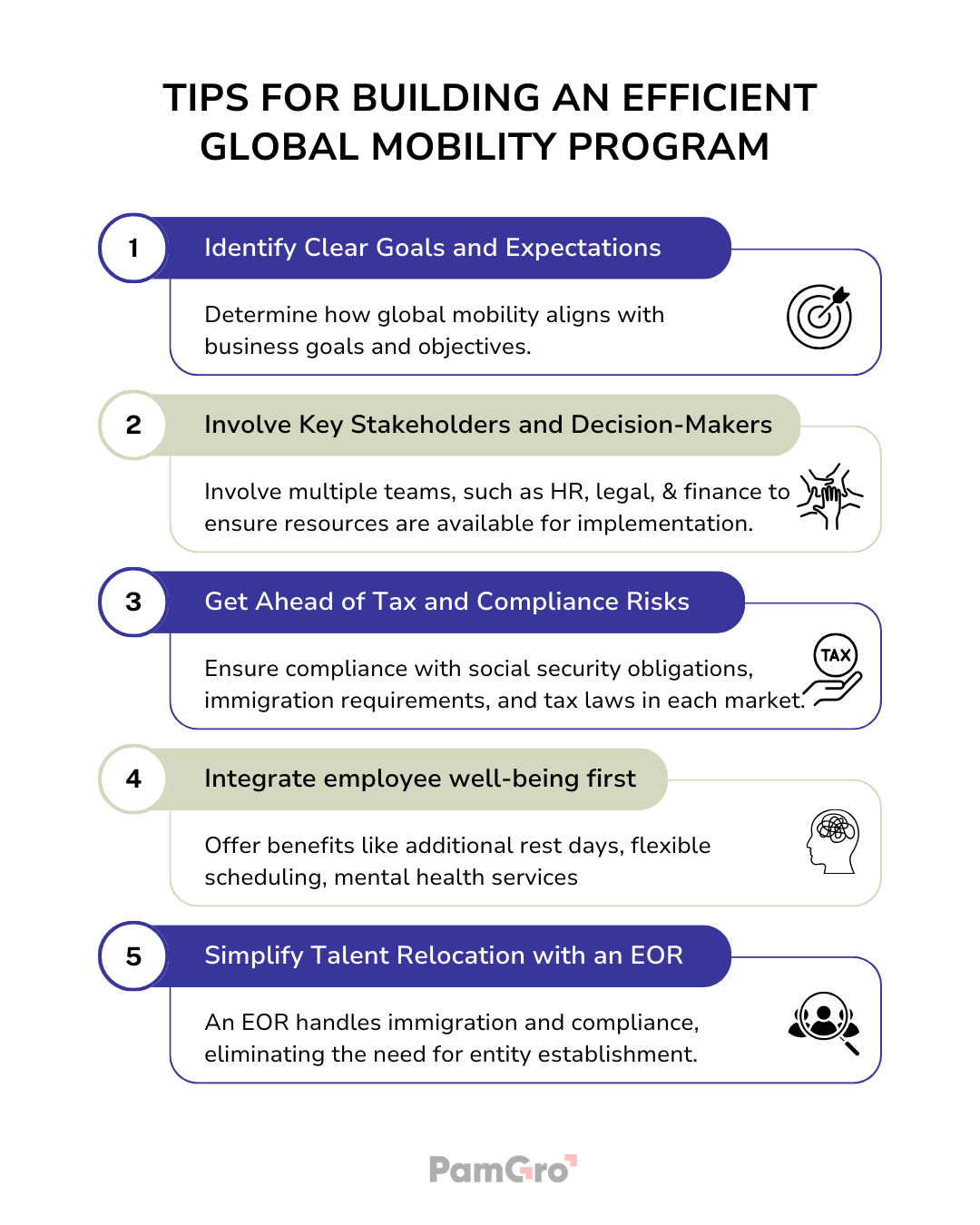
Establish Clear Goals and Expectations
Align Global Mobility for Success: Consider these key questions to ensure your program drives business objectives.
- What problems can global mobility solve?
- What additional benefits will it bring?
- Will entity establishment be part of the strategy?
- Which employees are eligible for relocation?
Involve Key Stakeholders and Decision-Makers
Global mobility strategies involve multiple teams, such as the HR team, legal, and finance. Maintain open communication to ensure alignment with their capabilities and goals. Involve high-level executives for long-term insights and consult with ground-level teams to ensure resources are available for implementation.
Get Ahead of Tax and Compliance Risks
Before venturing abroad, ensure compliance with social security obligations, immigration requirements, and local employment and tax laws in each market. Consult your legal team for guidance and consider partnering with international tax and immigration experts to navigate complex regulations and minimize compliance risks during your global expansion.
Put Employees First
Employee well-being is crucial for talent development and retention, especially for those working across borders. Offer employee benefits like additional rest days, flexible scheduling, mental health services, and opportunities to connect with colleagues or other expats.
Simplify Talent Relocation with an EOR
Partnering with an Employer of Record (EOR) simplifies global mobility. An EOR handles immigration and compliance, eliminating the need for entity establishment and allowing companies to attract, support, and retain mobile employees worldwide.
The Future of Global Mobility
1. Increased Remote Work
Hybrid Work Models: The shift towards remote work has fundamentally altered global mobility strategies. Many organizations are now adopting hybrid work models that blend remote and in-person work. This approach provides employees with the flexibility to work from anywhere while maintaining essential connections with their teams and the company culture.
Global Talent Pool: By embracing remote work, companies can hire talent from anywhere in the world without requiring immediate relocation. This widens the talent pool and allows organizations to attract and retain top talent regardless of geographic constraints.
Example: A tech company might allow its software developers to work remotely from different countries, using digital collaboration tools to stay connected. Periodic in-person meetings or team-building events can help maintain a cohesive team environment.
2. Focus on Sustainability
Reducing Environmental Impact: Organizations are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of frequent relocation. To mitigate this, they are adopting practices such as virtual assignments, reducing the need for physical travel, and encouraging the use of eco-friendly transportation options when travel is necessary.
Sustainable Business Practices: Companies are integrating sustainability into their broader business practices. This includes promoting energy-efficient housing for relocated employees, supporting remote work to minimize travel, and implementing policies that support long-term environmental goals.
Example: A multinational corporation might encourage employees to use public transportation or electric vehicles for local travel and offer incentives for sustainable housing options. Virtual assignments can be prioritized to reduce the carbon footprint associated with the physical relocation process.
3. Enhanced Employee Well-being
Comprehensive Support: Mental health and well-being have become central to global mobility strategies. Companies are now providing extensive support to their employees, including mental health resources, access to counseling services, and initiatives aimed at promoting a healthy work-life balance.
Work-Life Balance Initiatives: Organizations are recognizing the importance of maintaining a balance between work and personal life, especially for employees on international assignments. Initiatives such as flexible work hours, additional rest days, and family support programs are becoming more common.
Example: An international firm might offer relocated employees access to local mental health services, provide regular wellness check-ins, and offer flexible working hours to help them adjust to their new environment and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
4. Technological Advancements
AI for Compliance Management: Advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, are being utilized to manage compliance issues more effectively. AI can help ensure that companies adhere to various immigration, tax, and employment laws across different jurisdictions.
Data Analytics for Program Evaluation: Data analytics tools evaluate the effectiveness of global mobility policy and programs. By analyzing data on employee performance, relocation costs, and satisfaction levels, companies can make informed decisions and optimize their mobility strategies.
Virtual Reality for Cultural Training: Virtual reality (VR) is being employed to provide immersive cultural training for employees before they relocate. This technology helps employees acclimate to new cultural environments, reducing the adjustment period and improving overall assignment success.
Example: A global company might use AI-powered tools to automatically track and manage visa and tax compliance for employees working in different countries. VR can be used to simulate cultural scenarios, helping employees better understand and adapt to their new surroundings
PamGro: Simplifying Global Mobility Program
PamGro enables seamless global mobility through its comprehensive suite of services, ensuring compliant and efficient management of international talent. With a client-centric approach, PamGro offers tailored Professional Employer Organization (PEO) and Employer of Record (EOR) services, facilitating the hiring, onboarding, and payroll processes across multiple countries.
Leveraging advanced technology, PamGro provides support for work permits, immigration, and regulatory compliance, ensuring smooth transitions for employees. The dedicated relationship managers ensure personalized assistance, making PamGro an ideal partner for managing global mobility effectively and efficiently.
Conclusion
Global mobility is a critical component of modern business strategy, enabling organizations to leverage international talent and expand into new markets. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and best practices associated with global mobility, companies can create effective programs that support both business growth and employee satisfaction. As the international landscape continues to change, staying ahead of emerging trends and adapting to new realities will be crucial to the success of global mobility initiatives.
Payroll Solutions Unrivalled since 15 Years








