Global Workforce GlossaryVirtual Employee
Global businesses today are increasingly relying on virtual teams to access top talent, optimize costs, and maintain agility. A “virtual employee” allows companies to expand beyond geographic constraints, including remote location operate across time zones, and tap into diverse skill sets without establishing a local office. Virtual employees also enable businesses to maintain operations uninterrupted during emergencies or natural disasters. Understanding how virtual employees work, how to hire, manage, and engage them effectively, is crucial for any organization aiming to scale internationally. This guide answers the most common questions about virtual teams and staffing
Table of Contents
- What is co-employment?
- What are co-employment laws?
- Why is co-employment a risk?
- What are co-employment rules
- Co-employment do’s and don’ts
- How does co-employment work?
- What is the difference between co-employment and joint employment?
- Co-employment vs PEO
- Co-employment vs employee leasing
- Is co-op considered a full-time employee?
- Is it illegal to work for two jobs in the same industry?
- Co-employment examples
- Practical Case Study Example
- PamGro and Co-employment: Your Global Partner
What Is a Virtual Employee?
A virtual employee is a professional who works remotely for a company, often from a different city or country, using digital communication tools to complete tasks.
Unlike traditional in-office staff, virtual employees may be full-time, part-time, or contracted through virtual staffing services. They can work from various locations such as home, co-working spaces, or any place with internet access.
They rely on platforms like Slack, Zoom, and project management tools to collaborate. Companies often use an efficient Employer of Record (EOR), like PamGro, to manage contracts, local compliance, payroll, and benefits, making remote hiring seamless. Virtual employees allow businesses to tap into a global talent pool while minimizing overhead. Common tasks for virtual employees include data entry, IT troubleshooting, customer service, web design, and social media management.
How to Hire a Virtual Employee
Hiring virtual employees involves clear hiring planning, assessment, and structured onboarding.
Step 1: Define role and expectations – Outline deliverables, hours, time zone requirements, schedule and remote collaboration needs.
Step 2: Source talent – Post on global job boards, professional networks, or use virtual staffing and EOR services like PamGro to access qualified candidates worldwide.
Step 3: Evaluate remote skills – Conduct interviews focusing on autonomy, communication, digital proficiency, and time management.
Step 4: Draft a compliant contract – Cover deliverables, data protection, intellectual property, local labor laws, and benefits.
Step 5: Structured onboarding – Provide clear goals, assign a mentor, set milestones, and ensure access to necessary tools. The hiring process for virtual employees is typically faster and more cost-effective than for traditional employees.
This approach reduces time-consuming administrative tasks while ensuring you hire the best talent globally, saving you money. Many remote workers report higher productivity due to fewer office distractions and more flexibility in their working hours. Hiring virtual employees can lead to reduced operational costs since they do not require office space.
How to Become a Virtual Employee
To become a virtual employee, individuals need to adapt to remote workflows and develop skills that ensure productivity and trust.
- Remote-ready skills: Communication, time management, and proficiency in collaboration software (Asana, Trello, Zoom).
- Professional setup: Reliable internet, ergonomic workspace, and backup systems.
- Portfolio and experience: Highlight projects showing autonomy, digital collaboration, and results delivery.
- Self-discipline: Ability to meet deadlines independently and communicate proactively.
- Employer selection: Target companies open to virtual staffing or working with EOR partners like PamGro, ensuring smooth contracts and compliance for international hires.
- Employers must ensure that virtual employees have the necessary tools and equipment to be effective in their roles.
Success as a virtual employee is about demonstrating reliability, initiative, and the ability to deliver measurable results remotely. Virtual employees may experience challenges in separating work and personal time due to the overlap of their physical spaces. Regular employee satisfaction surveys can help understand a remote team’s efficacy.
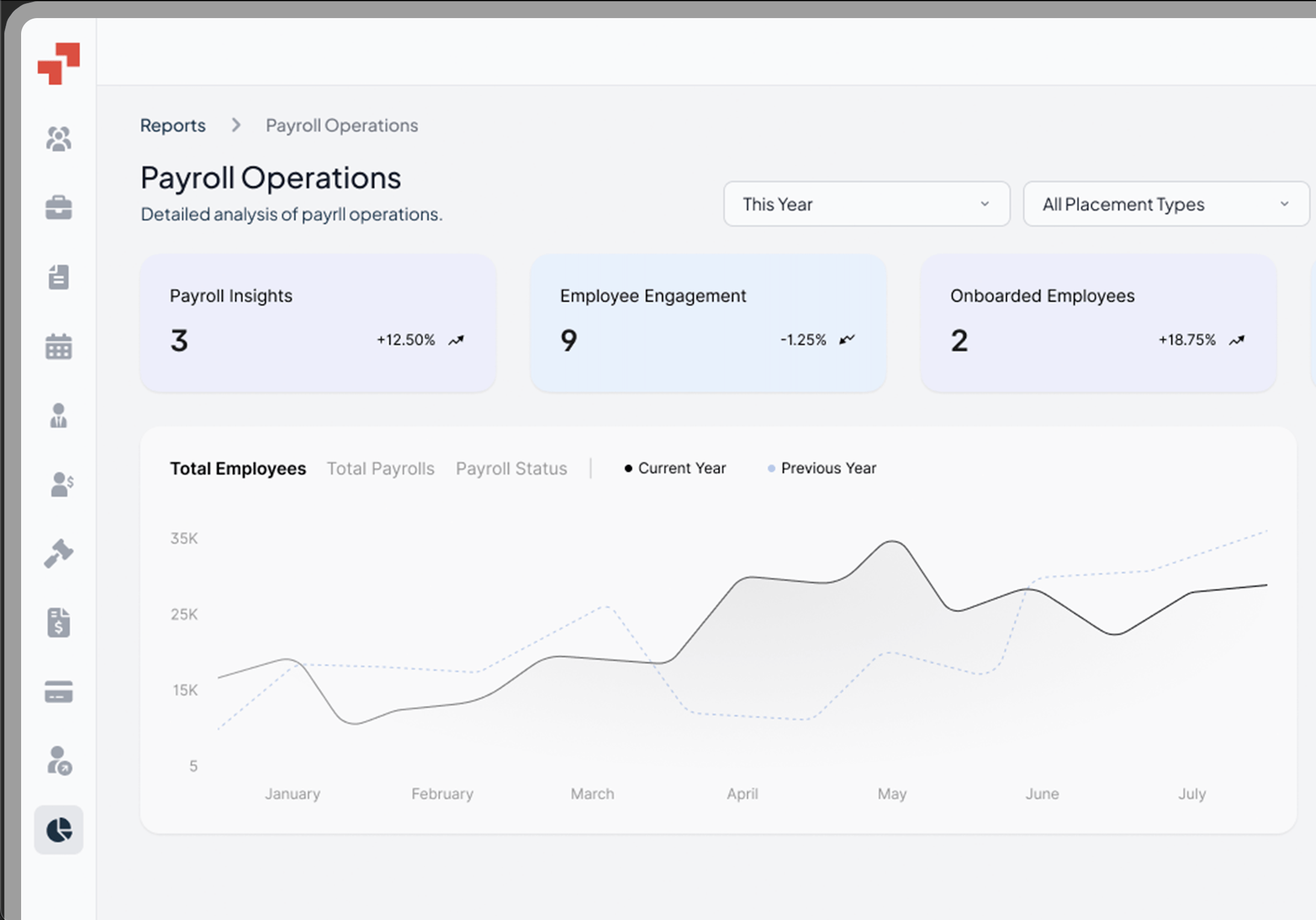
How to Monitor Virtual Employees
Monitoring virtual employees requires structured oversight without micromanaging. Communication issues can arise with virtual employees due to the lack of face-to-face interaction. Cultural differences can create challenges when team members speak different languages or have varying work decorum. Maintaining a strong company culture can be more difficult when managing a distributed team of virtual employees.
- Goal-based tracking: Define KPIs, milestones, and output expectations.
- Digital tools: Use project management (Asana, ClickUp) or time-tracking software to measure productivity.
- Regular check-ins: Weekly 1:1s, team huddles, and feedback sessions maintain engagement. Scheduling regular one-on-one meetings helps connect with virtual employees and provide support.
- Performance dashboards: Visual reports on progress and completion rates.
- Trust-first approach: Avoid micromanagement; encourage transparency and autonomy.
Clear documentation and processes are paramount when managing virtual teams.
Asynchronous communication tools are essential for effective collaboration among virtual employees across different time zones.
This combination ensures productivity, fosters engagement, and reduces the risk of isolation or misalignment.
What Are the Best Virtual Employee Engagement Activities?
Keeping virtual employees engaged is essential for productivity and retention, which ultimately helps in serving customers effectively. Hiring virtual employees can improve talent retention due to the flexibility they offer. Effective strategies include:
- Virtual coffee breaks or informal chats for casual connection.
- Team-building games and quizzes to boost morale.
- Peer recognition programs in chat platforms or team meetings.
- Skill-sharing sessions where employees teach each other a topic.
- Wellness initiatives like meditation or fitness challenges.
- Monthly virtual showcases highlighting achievements or personal stories.
Poor talent engagement may occur among virtual employees due to feelings of isolation.
Structured engagement keeps teams connected, motivated, and aligned, even when physically apart.
What Are Some Creative Virtual Employee Appreciation Ideas?
Appreciation for every new hire during their training strengthens loyalty and reduces turnover. Try:
- Personalized thank-you notes or packages delivered to home.
- Digital gift cards or vouchers for coffee, books, or streaming services.
- Surprise time-off or flexible scheduling rewards.
- Highlight achievements in newsletters or internal chats.
- Peer-nominated rewards system redeemable for gifts or perks.
- Video messages from leadership acknowledging contributions.
These small gestures improve morale and reinforce company culture in a virtual environment.
What Are Virtual Employee Services and How Do They Work?
Virtual employee services help companies manage remote talent efficiently. They include:
- Recruitment and onboarding: Identifying qualified candidates and integrating them.
- Payroll and benefits: Handling payments, local taxes, and benefits compliance.
- HR support: Managing contracts, legal compliance, performance reviews, and replacements.
- Ongoing administration: Ensuring seamless communication, governance, and operational support.
EOR partners like PamGro streamline these services, allowing companies to scale globally without creating legal entities in every country, similar to how full time employees might be managed.
What Are the Benefits of Hiring a Virtual Employee?
Hiring virtual employees offers strategic advantages:
- Access global talent unrestricted by geography.
- Cost efficiency: No office space, reduced utilities, and lower local overhead.
- Faster hiring cycles with fewer logistical constraints.
- Flexibility and scalability to ramp teams up or down.
- Diverse perspectives leading to innovation and creative problem-solving.
- Business continuity during disruptions, lockdowns, or travel restrictions.
Hiring virtual employees allows businesses to save on office space and equipment expenses.
This approach allows organizations to compete globally while maintaining operational efficiency. Virtual staffing helps small businesses and start-ups quickly expand operations to cover immediate needs.
Pros and Cons of Virtual Staffing
Pros of Virtual Staffing:
- Broader access to skilled talent.
- Lower operational costs.
- Increased flexibility and agility.
- Easy scalability and global reach.
- Improved employee satisfaction via autonomy.
- Diversity in hiring virtual employees can lead to a more innovative workforce.
Cons of Virtual Staffing:
- Potential communication delays.
- Risk of isolation or disengagement.
- Time zone differences complicate scheduling.
- Monitoring and accountability challenges.
- Legal, compliance, and payroll complexities.
- Limited spontaneous collaboration.
- Virtual employees have fewer opportunities for casual, in-person interactions with coworkers, which can make it harder to build rapport. Traditional employees benefit from regular informal interactions with colleagues, fostering team bonding and spontaneous brainstorming.
Using structured processes, collaboration tools, and EOR partners like PamGro mitigates data challenges effectively. The reliance on technology for remote work increases the risk of data breaches and cybersecurity threats.
What Is the Difference Between Remote and Virtual Employees?
Though often used interchangeably, subtle differences exist:
- Remote employee: Typically works from home or an alternate location but may be employed on local payroll.
- Virtual employee: Often fully integrated digitally, contracted via virtual staffing or EOR services, and may operate across borders.
Hiring virtual employees from other countries requires compliance with labor and tax laws specific to the employee’s location. Engaging contractors can offer flexibility for companies testing foreign markets but carries risks of misclassification.
Both rely on digital tools for collaboration, but virtual employees are often managed with international compliance considerations, making EOR services essential.
Example of a Virtual Employee
A SaaS company in London wants to expand its customer success team in different locations, including Latin America. They hire a virtual employee in Brazil through a virtual staffing service:
- Handles onboarding and support in Portuguese and Spanish.
- Accesses CRM, knowledge base, and Slack channels.
- Participates in weekly team meetings, logs tasks in Jira, and leads regional webinars.
- Payroll, benefits, and taxes are managed by an EOR partner.
Within six months, the startup sees a 30% increase in customer satisfaction in the LATAM region without setting up a local office—demonstrating the tangible impact of virtual employees.
Why PamGro Is Your Trusted Partner
Virtual teams are critical to global expansion, but building them effectively requires expertise in compliance, payroll, and local labor laws. PamGro’s global EOR services help businesses:
- Hire virtual employees across countries without establishing local entities.
- Manage payroll, contracts, taxes, and benefits efficiently.
- Onboard and integrate remote employees into your team seamlessly.
- Access the global talent pool while reducing administrative burdens.
Setting up a foreign entity for hiring virtual employees is a complex and costly process that requires understanding local laws.
Partnering with PamGro lets your business scale confidently, access top talent worldwide, and focus on growth instead of operational complexity. Book a free advisory call to explore how we can help you expand globally with ease.
Hire the Best Talent, Anywhere