Global Workforce GlossaryWhat is the Full Time Equivalent (FTE)?
Related Terms
Annualized Salary
Salaried Employee
Contingent Worker
Temporary Employee
Employee Cost Calculator
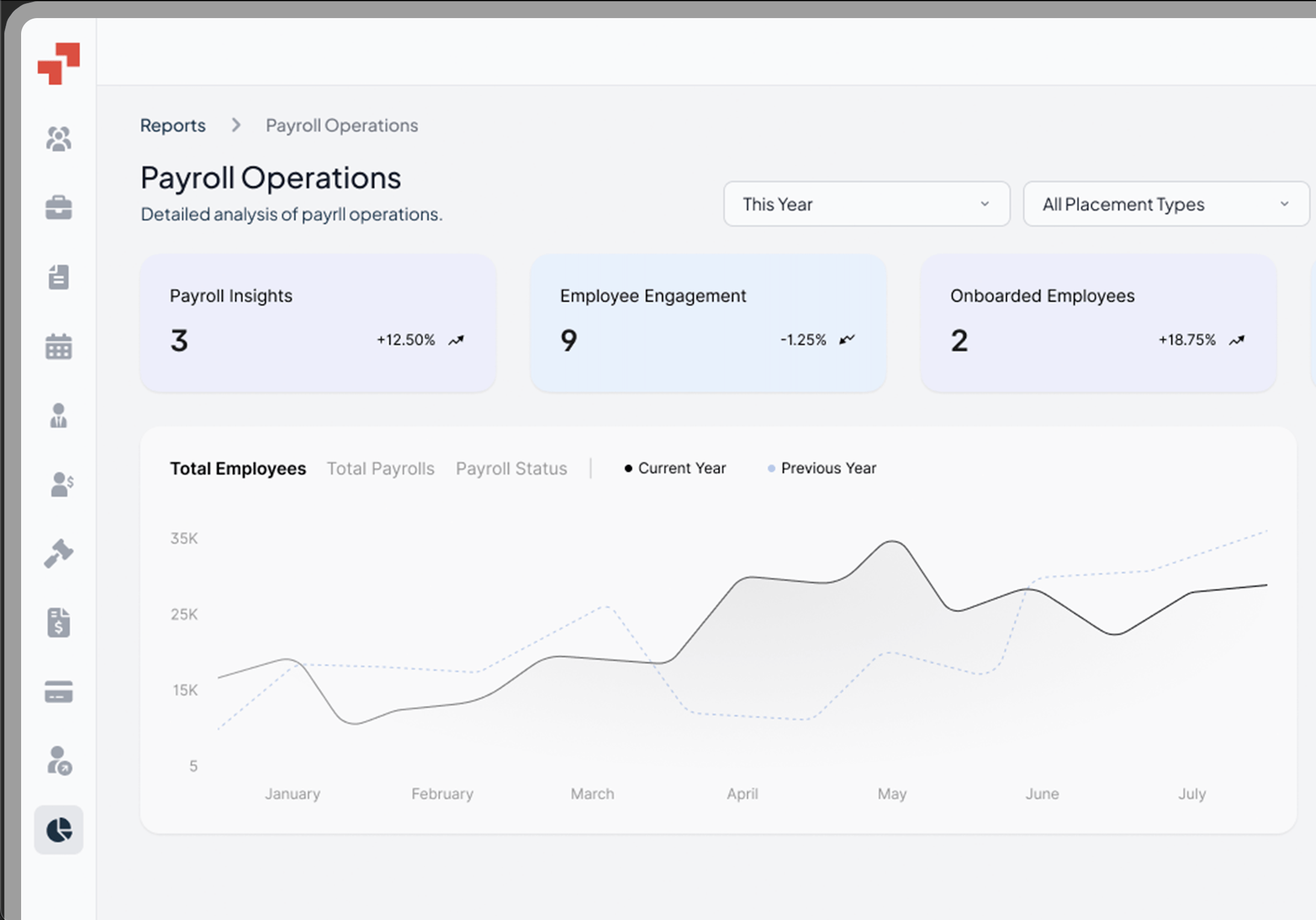
Full Time Equivalent (FTE) is a standardized way to measure employee workload by converting total hours worked into the equivalent number of full-time employees.
It is calculated by dividing actual hours worked by the standard full-time hours (typically 40 per week). This metric helps organisations compare part-time and full-time contributions on the same scale and assess overall staffing capacity.
FTE is a key metric for assessing workforce size and is used in various contexts such as budgeting, resource allocation, and compliance. It allows direct comparisons across differing schedules and workforce structures (e.g. a 0.5 FTE means half the standard full-time workload).
Table of Contents
- What is the full-time equivalent (FTE)?
- How to calculate full-time equivalent salary?
- What is the formula for calculating FTE?
- FTE Calculation Example
- Why is full-time equivalent important?
- What is the difference between full-time equivalent and a full-time employee?
- What is the difference between full-time equivalent and headcount?
- Applicable Large Employers
- Example Scenario
- FAQs
How to Calculate Full-Time Equivalent Salary?
The FTE salary is calculated based on the FTE ratio and the annual salary of a full-time equivalent.
Calculating the full time equivalent (FTE) is a four-step process:
- Count the Number of Hours Worked by Part Time Employees
- Count the Number of Hours Worked by Full-Time Employees
- Add the Number of Hours Worked by Both Part-Time and Full-Time Employees
- Divide the Total Hours Worked by All Employees by the Number of Available Full-Time Hours in a Year (2,080 Hours)
For example, if full-time is $100,000/year, an employee at 0.75 FTE would have a salary of 0.75 × $100,000 = $75,000.
What is the Formula for Calculating FTE?

You must define your “full-time hours standard” (e.g. 37.5, 40, or regionally mandated) before applying this formula.
This calculation uses the actual hours worked (i.e., the actual hours) by all employees. Knowing the number of hours worked and the average weekly hours is essential for ensuring the FTE calculation is accurate.
FTE Calculation Example
If full-time standard = 40 hours/week, and your team worked 600 hours total in a week, then: FTE = 600 ÷ 40 = 15.0, i.e. your staffing hours equal 15 full-time employees.
For example, if you have three employees: Employee A works 30 hours per week, Employee B works 20 hours per week, and Employee C works 10 hours per week. To find the total number of hours worked in a year, multiply each employee’s weekly hours by the number of weeks in a year (52 weeks), then sum the totals: (30 × 52) + (20 × 52) + (10 × 52) = 1,560 + 1,040 + 520 = 3,120 total number of hours worked annually by three employees.
An IT company has a support team of four employees. Two work full-time (40 hours each), one works 20 hours per week, and one works 15 hours per week.
Step 1 – Calculate total hours worked:
- Full-time employee 1 = 40 hours
- Full-time employee 2 = 40 hours
- Part-time employee = 20 hours
- Part-time employee = 15 hours
Total actual hours worked = 40 + 40 + 20 + 15 = 115 hours.
Step 2 – Apply the FTE formula:
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is calculated by dividing the total actual hours worked by the standard full-time hours (usually 40 hours per week).
So, the formula is:
FTE = Total actual hours worked ÷ Full-time hours (40)
Example:
If the total actual hours worked are 115, then:
FTE = 115 ÷ 40 = 2.875
This means the hours worked are equal to about 2.9 full-time employees.
Step 3 – Interpret the result:
Although there are four people in the support team, their combined workload is equivalent to 2.88 full-time employees.
Why is Full Time Equivalent Important?
FTE gives you a workload-adjusted view of workforce capacity. FTE is important because it enables organisations to align workforce planning with business objectives, ensuring that staffing levels are appropriate to meet strategic goals.
By accurately calculating FTE, companies can optimise:
- resource allocation across projects,
- manage labour costs,
- control payroll expenses more effectively.
This approach supports better budgeting, resource planning, and compliance thresholds (e.g. ACA in the US or labour laws in the EU) while avoiding distortions from headcount alone.
Additionally, understanding FTE helps organisations make informed decisions about hiring, training, and promotions, leading to improved operational efficiency.
What is the difference between a Full Time Equivalent and a Full-Time Employee?
A single full-time employee, or one employee classified as a full-time worker, always counts as 1.0 FTE under your defined standard, regardless of employment type. For example, a single employee working full-time hours is considered 1.0 FTE.
In contrast, a part-time employee’s FTE is calculated by comparing their actual hours worked to those of a full-time worker, so a part-time employee working 20 hours per week (when full-time is 40 hours) would count as 0.5 FTE.
- 40-Hour Work Week → 1.0 FTE
- 20-Hour Work Week → 0.5 FTE
The FTE metric can represent a single employee, such as one full-time worker, or a combination of part-time employees whose total hours add up to the equivalent of a single full-time employee.
What is the difference between Full Time Equivalent and Headcount?
Headcount equals the number of individuals employed, irrespective of hours. For FTE calculations, only considered employees are included; this typically excludes certain owners, contractors, or large shareholders who are not classified as employees for this purpose.
FTE converts all hours into the equivalent number of full-time workers. A company with 100 headcount might equal 80 FTE if many are part-time.
Applicable Large Employers
Applicable Large Employer (ALE) is an employer defined under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) as having an average of 50 or more full-time employees, including full-time equivalents (FTEs), during the previous calendar year. ALEs are required to offer affordable health coverage to full-time employees and their dependents and report coverage details annually to the IRS under the ACA’s employer shared responsibility provisions.
Example Scenario
You run a UK-EU operations hub, where full-time employment is defined as 37.5 hours/week. Suppose you have 10 full-time staff (each 1.0 FTE) and five part-time employees working 15 hours/week each.
To calculate the number of full-time equivalent employees, sum the work hours all employees work:
(10 × 37.5) + (5 × 15) = 375 + 75 = 450 hours. FTE = 450 ÷ 37.5 = 12.0 FTE.
Your headcount is 15, but your labor capacity is 12 full-time equivalents. This calculation is typically based on the previous calendar year to ensure legal compliance and meet legal requirements.
FAQs
What does FTE 50% mean?
FTE 50% means an employee performs half the workload of a full-time standard (i.e. 0.50 FTE). This means the employee works 20 hours per week when the full-time standard is 40 hours per week. Their hours are 50% of your defined full-time hours.
What does FTE 1.0, 0.75, or 0.5 mean?
- 1.0 FTE: full-time workload
- 0.75 FTE: three-quarters of full-time
- 0.5 FTE: exactly half of full-time
Each is calculated relative to your defined full-time hours (e.g. 0.75 × 40 = 30 hours/week).
The FTE value indicates the proportion of a full-time workload an employee is assigned, which is important for compliance with federal laws such as the ACA, as it determines employer obligations and employee eligibility for healthcare coverage based on full-time equivalency calculations.
How is FTE calculated for a 12-hour shift?
If your full-time day is 8 hours, one 12-hour shift in a single week = 1.5 FTE. Alternatively, if your full-time standard is 12 hours/day, then that shift in a single week = 1.0 FTE. Choose your benchmark and compute the shift/standard, ensuring that your calculation is based on the hours worked within a single week.
What is 0.8 FTE of 37.5 hours?
If full-time is 37.5 hours/week, then 0.8 FTE = 0.8 × 37.5 = 30 hours/week.
The annual work hours for 0.8 FTE would be 0.8 × 37.5 × 52 weeks = 1,560 annual work hours.
How to calculate FTE from hours?
Sum all employees’ hours over the period → divide by your full-time hours standard (weekly, monthly or annually) → result = FTE. (E.g. 1,500 hours ÷ 40 = 37.5 FTE.) This calculation gives you the actual number of FTEs for the period.
Hire the Best Talent, Anywhere