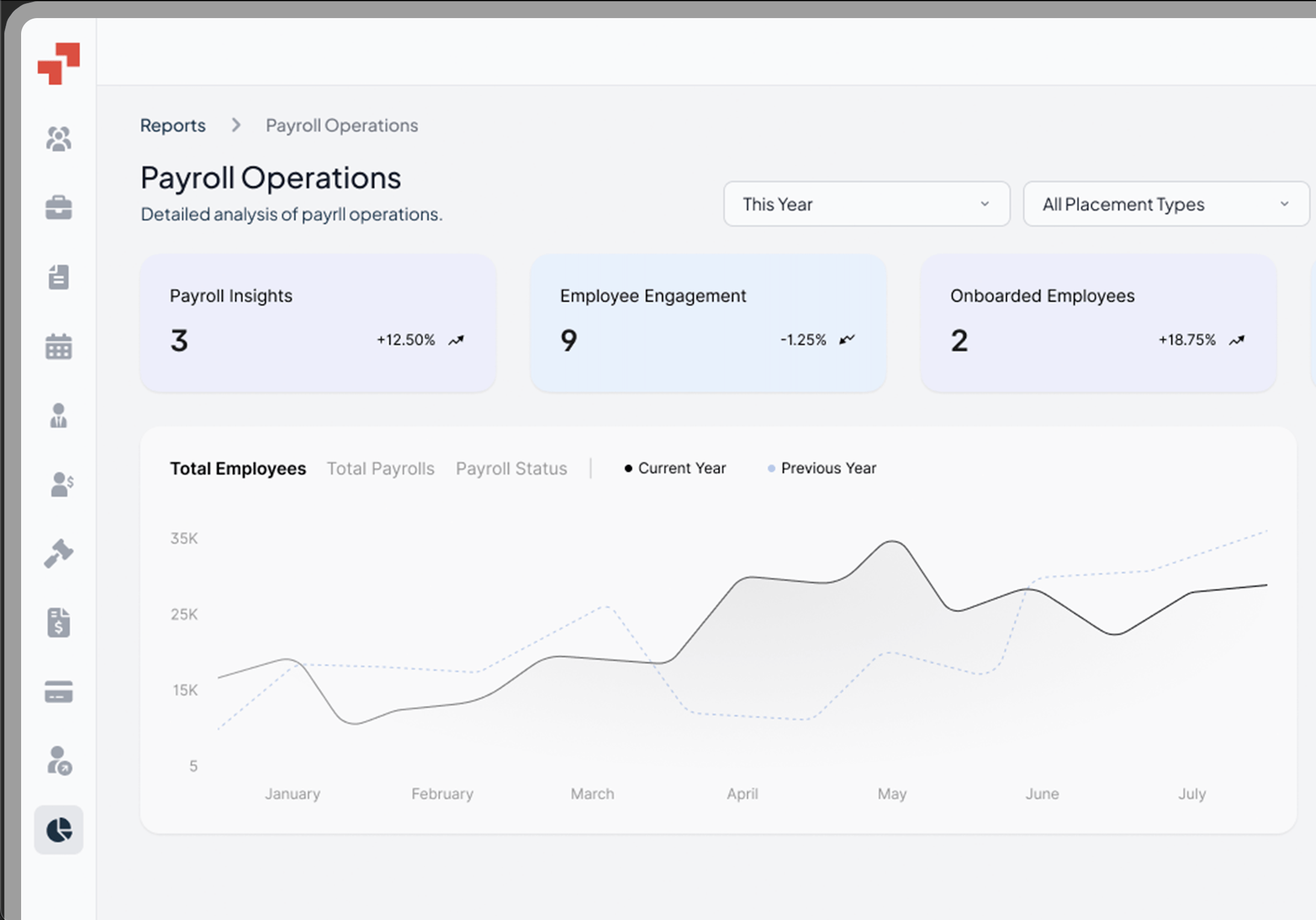
Global Workforce GlossaryWork Authorization
Hiring across borders brings immense opportunities — but also complex legal responsibilities. One of the most critical factors in international employment is work authorization. It ensures your company hires talent legally and compliantly, no matter where they’re based. This guide breaks down what work authorization means, how it works across countries, and what global employers must know to stay compliant while building distributed teams.
Table of Contents
- What is co-employment?
- What are co-employment laws?
- Why is co-employment a risk?
- What are co-employment rules
- Co-employment do’s and don’ts
- How does co-employment work?
- What is the difference between co-employment and joint employment?
- Co-employment vs PEO
- Co-employment vs employee leasing
- Is co-op considered a full-time employee?
- Is it illegal to work for two jobs in the same industry?
- Co-employment examples
- Practical Case Study Example
- PamGro and Co-employment: Your Global Partner
What is a Work Authorization?
Work authorization is the legal permission granted to non-citizens (foreign nationals), allowing them to work in a specific country.
In the U.S., this often comes in the form of an Employment Authorization Document (EAD), issued by the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) under the oversight of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. The EAD serves as proof that an individual is authorized to work for a defined period, though it does not grant permanent immigration status.
Work authorization requirements and processes vary by host country, and understanding the host country’s specific rules is essential for international employment.
Obtaining work authorization ensures compliance with labor laws and immigration laws, protecting both employers and employees from legal penalties. Work authorization can take various forms, such as permits, work visas, and permanent residency cards. Employers can verify authorization while planning workforce expansion efficiently
How to Renew Work Authorization
Renewing work authorization requires submitting Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization, to USCIS before the current authorization expires. Employment Authorization Documents (EADs) are valid for a specific period, which varies depending on the applicant’s immigration status and circumstances. Filing approximately 180 days in advance is recommended to avoid gaps in employment eligibility.
Certain categories, such as asylum seekers and TPS holders, may qualify for automatic work permit extensions of up to 540 days (Reuters). Employers should stay informed of processing times and regulatory updates.
To maintain compliance with employment laws and immigration regulations, it is essential to maintain accurate records of work authorization expiration dates and renewals. This ongoing documentation helps ensure organizations are maintaining compliance and avoid potential penalties.
How to Apply for Work Authorization
To apply, complete Form I-765 and submit it with supporting documents and the applicable filing fee, making sure to pay all applicable fees as required by the application process. Eligibility depends on immigration status, such as:
- Asylum seekers (asylum applicants may have specific procedures or timelines for applying for work authorization)
- F-1 students (OPT/CPT)
- H-4 visa holders
- TPS recipients
Ensure all information is accurate and complete. Keep copies of your application for records. Filing fees and eligibility criteria can be confirmed on USCIS’s official site. Some applicants may qualify for a fee waiver if they meet certain criteria, which can help reduce the financial burden.
How to Get Work Authorization in the U.S. Based on Immigration Status
Eligibility is tied to immigration status:
| Status | Work Authorization |
|---|---|
| Asylum Seekers | EAD after 150 days pending application |
| F-1 Students | Optional Practical Training (OPT) or Curricular Practical Training (CPT) |
| H-4 Visa Holders | EAD if spouse is H-1B and certain conditions are met |
| TPS Holders | EAD valid during TPS period |
Filing Form I-765 with accurate documentation ensures timely approval. Processing times may vary depending on status and USCIS workload
Types of Work Authorization in the U.S.
Work authorization can be categorized as follows:
- Employment Authorization Document (EAD): General work permit for eligible non-citizens.
- Work Visas (H-1B, L-1, O-1): These are nonimmigrant visas that allow foreign workers to be employed in the U.S. for a specific employer. Some of these visas require proof of specialized skills or qualifications, and employment is often tied to a specific employer or a specific employer incident.
- Green Card (Permanent Residency): Green card holders have permanent work authorization and can work for any employer without additional permits.
- OPT/CPT for F-1 Students: Limited work authorization in the field of study.
Employers must understand their responsibilities when hiring foreign workers, especially when work authorization is tied to a specific employer or a specific employer incident.
How to Get an Employment Authorization Document (EAD) Card
The EAD card is issued after USCIS approves Form I-765. Typically valid for 1–2 years, it can be renewed. Submit your renewal application before the current EAD expires to avoid interruptions.
The card itself acts as proof of the right to work and is required by employers during Form I-9 verification.
How Do Employers Verify Work Authorization?
Employers must complete Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification, for all new hires to verify each employee’s work authorization. This involves reviewing documents proving identity and employment authorization.
Optionally, employers can use E-Verify, an online tool confirming that employee records match federal databases. HR professionals play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with work authorization laws and procedures. Ensuring compliance helps avoid legal penalties and ensures a smooth global hiring process. By ensuring compliance with verification requirements, organizations can avoid penalties and maintain a lawful workforce.
Work Authorization vs. Green Card: How do they Differ
| Aspect | Work Authorization (EAD) | Green Card |
|---|---|---|
| Validity | Temporary, linked to status | Permanent residency |
| Work Rights | Restricted to authorized periods | Unrestricted employment with permanent work authorization |
| Family Sponsorship | Not included | Eligible to sponsor relatives |
| Immigration Status | Does not confer status | Confers permanent resident status |
While EAD may be a step toward a green card, it is primarily temporary and conditional.
What is the Difference Between Work Authorization and Work Permit
- Work Authorization: Legal permission to work, which can be obtained through various forms, including permits and work visas, depending on the individual’s status and country-specific requirements.
- Work Permit: Physical proof of authorization, such as an EAD card, or official documents like work permits and work visas that permit legal employment.
Individuals must obtain work authorization before starting employment to ensure legal compliance.
Employers must verify that employees hold proper authorization to maintain legal compliance.
What Role Do Employers Play in Work Authorization?
Employers are responsible for:
- Verifying all employees’ eligibility via Form I-9
- Retaining records for audits
- Using E-Verify for additional verification (optional)
- Staying updated on immigration regulations
- Maintaining accurate records of employees’ work authorization documents, including expiration dates
Proper management prevents fines and ensures a legally compliant workforce. Maintaining compliance with immigration regulations is an ongoing responsibility for employers.
Legal Compliance in Work Authorization
Ensuring legal compliance in work authorization is essential for building a lawful workforce. Employers must verify each employee’s employment authorization document (EAD), passport, and social security number to confirm eligibility to work. Monitoring expiration dates and renewing documents as needed prevents lapses in authorization.
Adhering to immigration laws and regulations protects the organization from fines, legal consequences, and reputational harm. Maintaining accurate records and staying updated on current immigration requirements ensures ongoing compliance and safeguards the business from unnecessary risks.
Avoiding Legal Issues in Hiring
To minimize legal risks, employers should verify work authorization and immigration status, including documents like Form I-766, and confirm eligibility through USCIS or relevant authorities. Employers must avoid discrimination based on visa or citizenship status, ensuring equal opportunity for all candidates.
Special attention is needed for international students on OPT to maintain compliance. Keeping accurate records and regularly reviewing work authorization documents helps prevent legal issues and supports a lawful, diverse, and inclusive workforce
Expert Support and Resources
Navigating work authorization and immigration laws can be complex, but employers have access to expert support and resources. The USCIS provides guidance on employment authorization documents, work visas, and permits, while immigration attorneys can help ensure full compliance.
Online resources offer up-to-date information on forms and regulations, helping employers stay informed and maintain legal compliance. Leveraging these tools allows businesses to confidently manage work authorization and support a diverse, authorized workforce.
Practical Example: Hiring Foreign Nationals with Work Authorization
A U.S. SaaS startup hired developers from India on H-1B visas. To ensure continuous employment, HR managed EAD applications for employees transitioning from F-1 OPT status. Verification via Form I-9 and E-Verify ensured compliance. By leveraging PamGro’s EOR services, the startup streamlined payroll, benefits, and global compliance without creating foreign entities, reducing administrative overhead and legal risk.
PamGro: Your Global Employment Partner
PamGro simplifies global hiring through Employer of Record services. We handle:
- Work authorization compliance
- Payroll and benefits administration
- Legal and tax obligations
- Local employment regulations
Partnering with PamGro enables companies to hire top talent worldwide efficiently and legally, focusing on growth while we manage the complexities of international employment.
FAQs About Work Authorization
Only if you have another valid work visa or a green card
Typically 1–2 years, depending on status.
Yes, via Form I-765 before expiration
Generally yes, unless restricted by visa or category.
Stop working immediately until renewal approval.
Hire the Best Talent, Anywhere