Global Workforce GlossaryCompliance Management
Related Terms
HR Compliance
Payroll Compliance
GDPR Compliance
Compliance Risk Management
International Employment Law
In today’s business environment, keeping up with regulations and industry standards can be challenging. Effective compliance management often involves balancing legal requirements with operational needs, ensuring processes run smoothly while minimizing risks. Companies are increasingly looking for ways to integrate compliance into daily workflows without slowing down growth. It’s less about rules and more about creating systems that support ethical and efficient business practices.
Table of Contents
- What is co-employment?
- What are co-employment laws?
- Why is co-employment a risk?
- What are co-employment rules
- Co-employment do’s and don’ts
- How does co-employment work?
- What is the difference between co-employment and joint employment?
- Co-employment vs PEO
- Co-employment vs employee leasing
- Is co-op considered a full-time employee?
- Is it illegal to work for two jobs in the same industry?
- Co-employment examples
- Practical Case Study Example
- PamGro and Co-employment: Your Global Partner
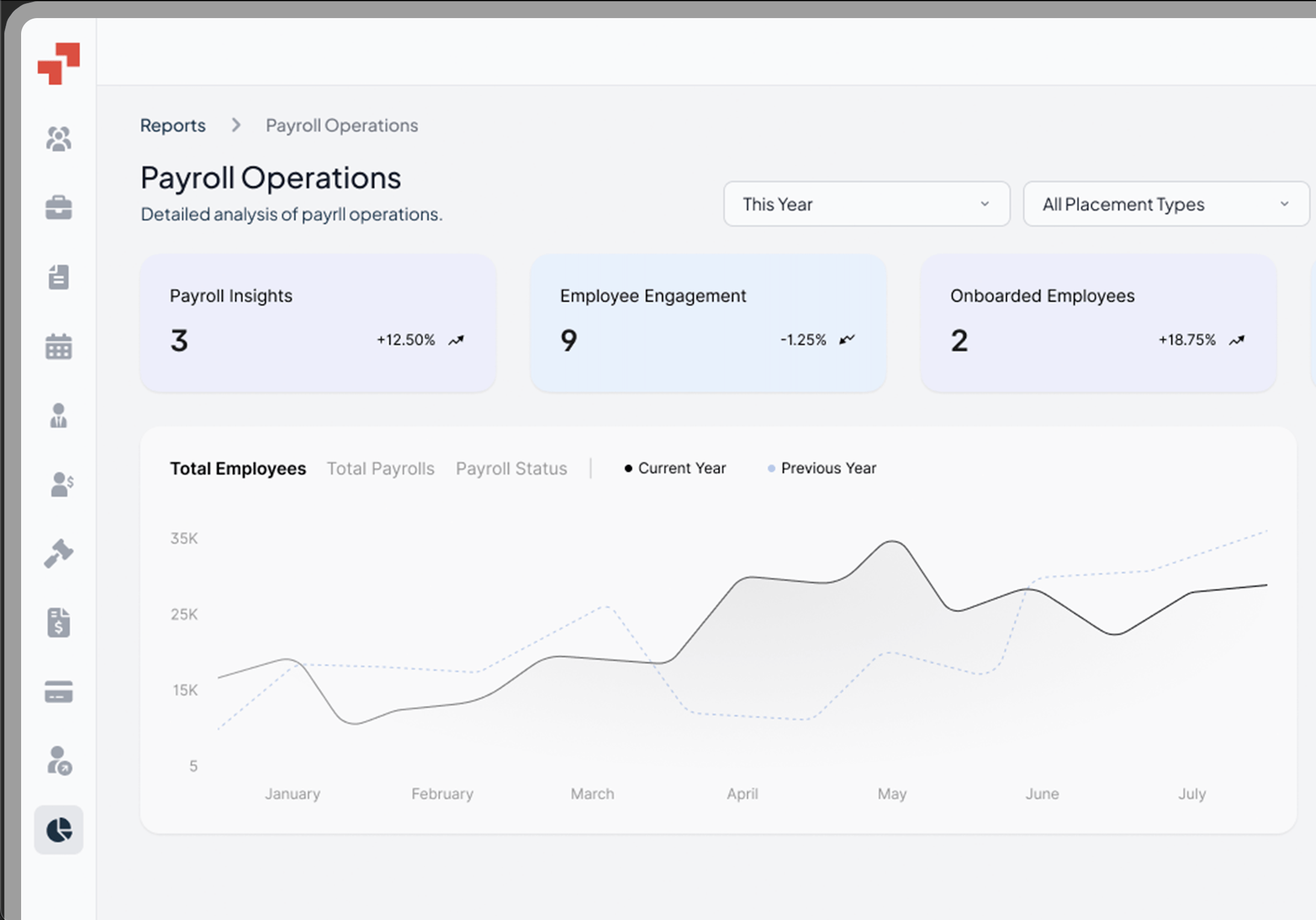
What is a Compliance Management System?
A compliance management system (CMS) is a structured framework that helps organizations ensure their operations meet legal, regulatory, and internal policy requirements.
It provides a centralized way to monitor, assess, and enforce compliance across different business units, minimizing risks of violations or penalties.
A CMS typically combines policies, procedures, reporting mechanisms, and technology platforms to streamline compliance oversight. A well-designed CMS goes beyond checking boxes. It builds a culture of accountability where compliance efforts are integrated into daily operations.
Businesses often rely on it to manage audits, conduct employee training, track compliance risks, and demonstrate adherence to industry standards. By formalizing processes, a CMS also improves transparency, which can be critical during government inspections or internal reviews. According to the U.S. Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, regulators expect financial institutions to have a documented and effective CMS (OCC.gov).
What is a Compliance Management Program?
A compliance management program is the organized set of activities and processes an organization uses to maintain compliance. While a CMS provides the system or structure, compliance management refers to the practical execution—such as conducting risk assessments, monitoring activities, and implementing training.
Effective programs usually cover multiple dimensions: data protection, workplace safety, environmental regulations, and anti-bribery rules. They’re often tailored by industry. For example, healthcare programs may focus heavily on HIPAA, while financial services emphasize anti-money laundering (AML). Programs should evolve as regulations change and as businesses expand into new regions. A strong compliance program not only prevents violations but also builds trust with employees, customers, and regulators.
How Does Compliance Management Software Work?
Compliance management software is a digital solution designed to automate compliance tracking, reporting, and monitoring. Instead of relying on spreadsheets or manual oversight, businesses use software to centralize policies, assign tasks, monitor regulatory updates, and prepare for compliance audits.
Modern platforms include features like access control, policy distribution, compliance dashboards, and risk scoring. For global companies, software helps track country-specific laws, tax compliance, and data security mandates such as GDPR. By reducing manual errors and increasing visibility, compliance software improves efficiency while lowering the cost of compliance. Gartner research notes that automation is one of the fastest-growing segments in governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) technology, reflecting its importance for modern organizations.
What Types of Compliance Management Tools Exist?
Compliance management tools are the resources—both digital and procedural—that organizations use to ensure compliance. These include audit checklists, reporting templates, policy management systems, compliance calendars, and whistleblower hotlines.
For global businesses, tools often integrate with HR, payroll, and EOR (Employer of Record) systems to ensure local labor law compliance. Advanced tools also leverage AI to monitor for anomalies, automate reporting, and flag emerging risks. The best compliance tools align with an organization’s industry requirements and risk profile, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks. Regular updates and user-friendly dashboards make them practical for busy compliance teams.
How Can Companies Mitigate Compliance Management Risks?
Compliance management risk refers to the possibility of an organization failing to meet regulatory, contractual, or ethical obligations. Risks may include fines, legal penalties, reputational harm, and operational disruption.
Common sources of compliance risk include:
- Rapidly changing regulations across different jurisdictions
- Data privacy violations
- Inadequate employee training
- Poor internal controls
For companies hiring globally, compliance risk expands significantly—each new country may have unique labor, tax, and reporting obligations. A robust compliance risk management strategy involves proactive monitoring, internal audits, and continuous training. According to PwC’s 2024 Global Risk Survey, regulatory compliance remains among the top five risks reported by executives worldwide.
What Do Compliance Management Services Offer?
A compliance management service is an outsourced solution where third-party experts help organizations manage compliance. These services may include regulatory monitoring, audit preparation, training programs, and reporting assistance.
For global hiring, compliance management services often cover labor laws, payroll processing, and employee classification. Partnering with a compliance service reduces internal burden, ensures adherence to changing laws, and mitigates compliance management challenges and risk exposure. It’s particularly valuable for small and mid-sized companies that lack in-house compliance departments. By leveraging expertise, organizations can focus on core growth while staying legally protected.
Compliance Management vs. Risk Management: What is the Difference?
Compliance management ensures organizations follow laws and policies, while risk management identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential threats to business objectives. Though different, the two disciplines are interconnected.
Compliance management focuses on meeting external standards (laws, regulations, certifications), whereas risk management takes a broader view, covering strategic, financial, and operational risks. For instance, compliance management ensures GDPR requirements are followed, while risk management evaluates the broader impact of data breaches on customer trust. Forward-thinking organizations integrate both functions, creating resilience by aligning compliance with overall enterprise risk management frameworks.
Understanding Compliance vs. Quality Management
Compliance management ensures adherence to external rules, while quality management ensures products and services meet internal standards and customer expectations.
For example, a pharmaceutical company’s compliance management ensures FDA regulations are followed, while quality management ensures that each batch meets internal safety benchmarks. While compliance often has a legal or regulatory driver, quality management is about continuous improvement. Yet, they overlap significantly—failing quality standards can result in compliance violations, and vice versa. Companies that integrate quality and compliance systems can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
What are the Three Types of Compliance?
Compliance is generally categorized into three types:
- Regulatory Compliance – Following laws and regulations (e.g., tax codes, labor laws).
- Corporate Compliance – Adhering to internal company policies and procedures.
- Third-Party Compliance – Ensuring vendors, partners, and contractors meet required standards.
Each type plays a critical role in protecting organizations. Regulatory compliance avoids legal penalties, corporate compliance ensures internal integrity, and third-party compliance safeguards supply chain reliability. Many industries, such as finance and healthcare, require organizations to demonstrate all three types during audits or certifications.
What is Compliance Management, and How to Implement It?
Compliance management is the practice of designing, executing, and monitoring systems that ensure an organization operates within legal, ethical, and regulatory boundaries. Implementation involves a step-by-step process:
- Identify applicable laws and regulations
- Develop policies and procedures
- Implement compliance tools and training
- Monitor performance and risks
- Conduct regular audits and reviews
Organizations often appoint a compliance officer or team to oversee implementation. For international companies, the process includes adapting compliance frameworks to each jurisdiction. Successful implementation reduces penalties, fosters trust, and creates a culture where compliance is viewed as an enabler, not just a restriction.
Why Is Compliance Management Important for an Organization?
Compliance management is essential because it protects organizations from legal penalties, financial losses, and reputational harm. It ensures ethical operations, builds stakeholder trust, and enables smooth international growth by maintaining compliance .
For organizations expanding globally, compliance management ensures adherence to foreign labor laws, tax obligations, and data protection mandates. Without it, businesses risk shutdowns, lawsuits, loss of licenses, and other potential compliance risks. Moreover, strong compliance programs can enhance operational efficiency by standardizing processes. As regulators worldwide tighten enforcement, compliance is no longer optional—it’s a competitive differentiator that demonstrates responsibility and reliability.
Example of Compliance Management
A multinational tech startup expanding into Germany hires employees directly without setting up a local entity. Without compliance management, it risks violating German labor laws, tax regulations, and employee protections. By adopting a compliance management system, the startup tracks employment contracts, ensures payroll accuracy, and stays aligned with EU data privacy laws.
This example highlights how compliance management prevents costly errors, avoids penalties, and builds credibility with regulators. In practice, it may include automated payroll compliance software to meet compliance requirements , legal consultation, and structured training programs. By proactively managing compliance, the organization not only avoids risks but also enables faster, safer growth.
Practical Case Study on Compliance Management
Imagine a U.S.-based SaaS company planning to expand into India and Brazil. Instead of establishing subsidiaries, the company leverages a compliance management framework supported by EOR services. The system tracks each country’s labor laws, ensures timely tax filings, and enforces workplace policies aligned with local standards.
Within six months, the company successfully onboards 30 employees across two continents without facing compliance delays. Regulatory audits confirm adherence to local labor codes, avoiding potential fines. Beyond cost savings, compliance management gives executives confidence to scale further. By embedding compliance into operations, the company grows globally while maintaining trust with regulators and employees alike
PamGro and Compliance Management
Expanding internationally multiplies compliance challenges—every new country adds labor laws, payroll rules, and tax complexities. PamGro simplifies compliance management by acting as your Employer of Record (EOR) partner. We handle global payroll, employee classification, tax compliance, and benefits administration while ensuring adherence to security standards —so your business can focus on growth, not red tape.
With PamGro, you gain:
- Local expertise in 100+ countries
- Automated compliance monitoring
- Reduced risk of misclassification and penalties
- Transparent onboarding and reporting tools
Compliance doesn’t have to be a barrier to global expansion. Partner with PamGro to navigate regulations with confidence, protect your business, and unlock new growth opportunities.
External Resources
Hire the Best Talent, Anywhere