Global Workforce GlossaryPayslip
A payslip is more than a salary summary; it’s a compliance tool, a record of employment, and a vital document for employees and employers alike. Understanding it fully ensures accurate payroll management, legal adherence, and seamless global operations.
Table of Contents
- What is a payslip?
- What does a payslip look like?
- When is a payslip generated and who issues it?
- Payslip vs. pay stub: What’s the difference?
- Payslip vs. paycheck: How do they compare?
- Can a payslip be used as proof of address?
- Why is a payslip important?
- What information is listed on a payslip?
- How to create and manage electronic payslips?
- Are employers required to provide payslips?
- Example of Payslip
- FAQs
What is a payslip?
A payslip is an official document issued by an employer detailing an employee’s earnings, deductions, and net pay for a specific pay period.
A payslip is also commonly called a ‘pay slip’ or ‘salary slip’ in different regions.
It serves as proof of salary, taxation, and statutory contributions, ensuring transparency between employer and employee while facilitating compliance with local labor and tax laws. Payslips are legally required in many jurisdictions and are subject to regulatory requirements. Payslips also support tax compliance for both employers and employees.
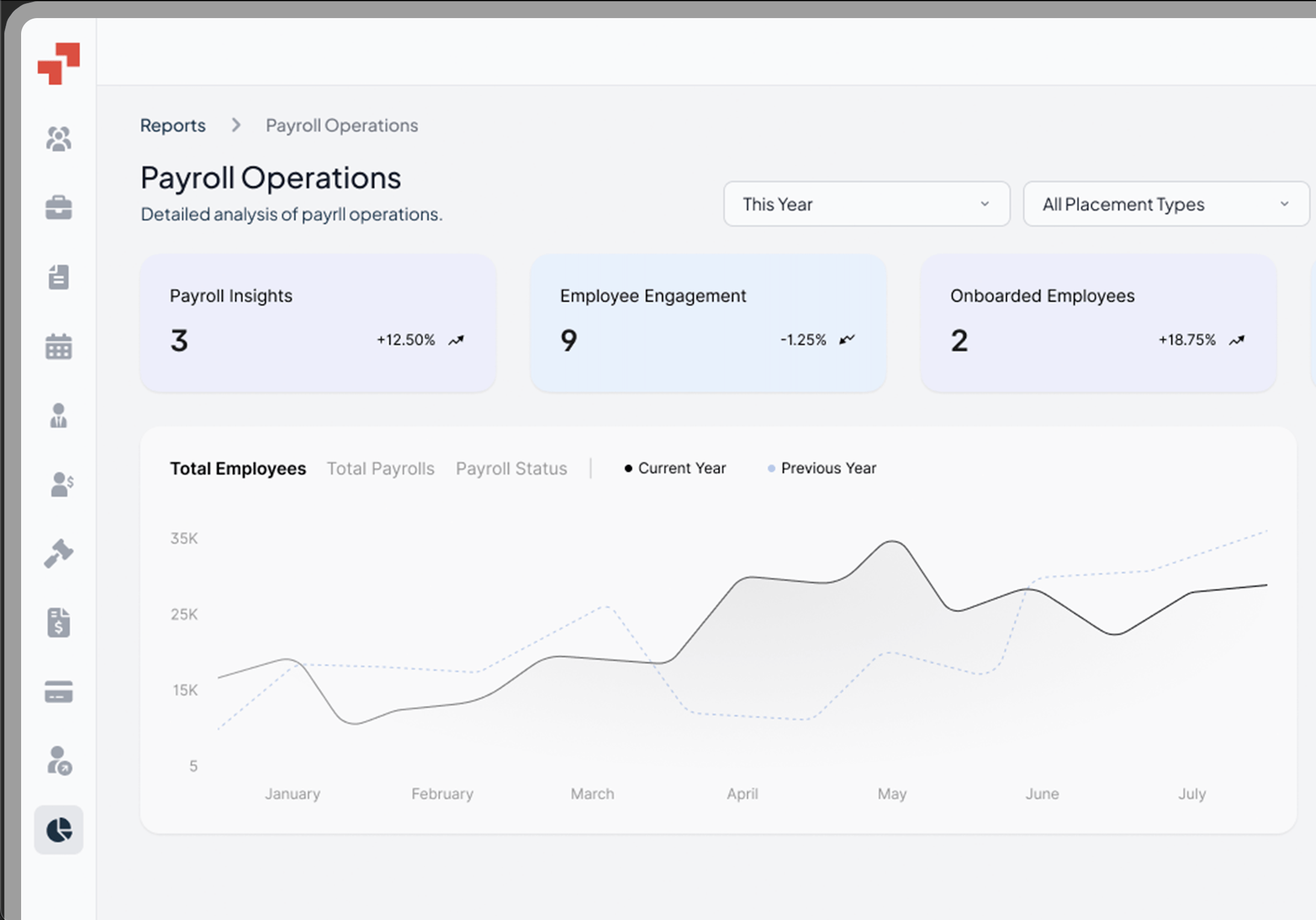
What does a payslip look like?
A payslip typically includes employee information (such as name, employee ID, and job designation)
Employer information (company name and identification), and contact details for both parties.
The current pay period, including the start and end dates, as well as the pay date.
Standard components are :
- Pay rate and hours worked (especially for hourly employees)
- Gross income
- Gross earnings
- Total income
- Total earnings
The payslip provides a detailed breakdown of the employee’s pay, including additional payments like overtime pay, bonuses, and allowances. It lists leave balances, retirement contributions, employer contributions, health insurance, and health insurance premiums.
Common deductions shown include employee’s tax information, state taxes, income tax, FICA taxes, wage garnishments, and other common deductions.
The actual amount or take-home pay (net salary) is the final amount the employee receives. Payslips and pay stubs often contain the same information, serving as a comprehensive record to help employees verify their compensation and statutory contributions.
When is a payslip generated, and who issues it?
Payslips are generated each payroll cycle, weekly, biweekly, or monthly by the employer or a payroll service provider. Employees receive payslips each time they are paid, and the frequency can vary depending on company policy or local regulations.
The payroll department is responsible for managing the payroll process and issuing payslips. They are usually issued alongside salary disbursement, digitally or in print, ensuring employees have timely access to compensation details and legal proof of income.
Payslip vs. pay stub: What’s the difference?
While both documents detail earnings and deductions, pay stubs and pay slips are commonly called by different names depending on the region.
A pay stub is often a simplified version accompanying a paycheck, primarily in the U.S., whereas a pay slip is a formal record, typically mandated by law in the UK, EU, and other regions, and includes comprehensive statutory information and employer details.
Despite these differences, pay stubs and pay slips usually contain the same information, such as earnings, taxes, and deductions, but the format and terminology may differ.
Payslip vs. Paycheck: How do they compare?
A paycheck represents the actual payment made to the employee, which may be issued as a physical paycheck, a physical check, or deposited directly into the employee’s bank account.
The employee’s paycheck is the actual transfer of funds, while the payslip is the detailed statement showing how that payment was calculated. The payslip itemises gross pay, deductions, and net pay, ensuring transparency and serving as a legal record of earnings.
Can a payslip be used as proof of address?
Payslips may sometimes serve as supplementary proof of residence, particularly if they include an employee’s home address. However, most jurisdictions require additional documentation utility bills or official correspondence, for formal address verification.
Why is a payslip important?
Payslips ensure legal compliance, document employee earnings, and support audits or tax reporting.
Payslips are essential for tax purposes and tax compliance, as they help ensure adherence to tax regulations. They are often required as proof of income when applying for bank loans or other financial products.
Payslips also help employees track salary, benefits, and deductions, and provide proof of income for loans, mortgages, or government benefits, reinforcing trust and transparency between employer and employee.
Additionally, payslips reflect adherence to the employment contract and play a key role in global payroll management for multinational organizations.
What information is listed on a payslip?
A payslip typically includes a detailed breakdown of the following: employer and employee details, pay period, gross salary, employee’s tax information, additional earnings such as bonuses, commissions, and overtime pay, common deductions (including taxes, social security, health insurance, and retirement contributions), net pay, and cumulative year-to-date totals.
Some regions also require tax identification numbers and statutory contributions for compliance.
How to create and manage electronic payslips?
Electronic payslips are generated using payroll software or HR platforms, ensuring secure distribution, legal compliance, and easy record-keeping. For companies managing global payroll, electronic payslips are especially important as they help ensure compliance with regulatory requirements across different countries.
Employers can automate issuance, maintain digital archives, and provide employees with encrypted access, reducing administrative overhead while meeting audit requirements.
Are employers required to provide payslips?
Yes. In most countries, including the UK (Employment Rights Act 1996) and EU states, employers are legally required to issue payslips for each pay period to comply with regulatory requirements.
In the U.S., while federal law doesn’t mandate payslips, many states require them, and employers often provide them voluntarily to maintain transparency
Example Scenario
Scenario: A U.S.-based SaaS company expands to Germany and hires its first local engineer. By leveraging a global payroll system, the HR team ensures accurate payroll processing and tax compliance across countries.
Issuing compliant electronic payslips, they record gross salary, social security contributions, and tax deductions. When the employee applies for a rental apartment, the payslip doubles as proof of income, satisfying both legal and practical requirements.
This digital approach minimizes errors, supports audit readiness, and reinforces employee trust while aligning with EU labor regulations.
FAQs
Where can I find or retrieve my payslip?
Employees can retrieve payslips from HR portals, payroll platforms, or directly from the employer. Many companies offer electronic access through secure logins, while physical copies may be available on request. Maintaining copies is recommended for tax, loan, or compliance purposes.
Hire the Best Talent, Anywhere